Metal fabrication is a critical process in the oil and gas industry, providing essential components and structures that support the exploration, extraction, and transportation of hydrocarbons.
As the demand for oil and gas continues to rise, so does the need for advanced metal fabrication techniques that ensure safety, efficiency, and durability.
In this blog article, we will explore about the applications of metal fabrication in the oil and gas sector, exploring its significance, the technologies involved, and future trends.
Understanding Metal Fabrication
Metal fabrication refers to the process of creating metal structures by cutting, bending, welding, and assembling various metal components. This process is vital in numerous industries, but it plays a particularly crucial role in oil and gas due to the demanding nature of operations in this field.
Key Processes in Metal Fabrication
- Cutting: Involves slicing metal sheets or components into desired shapes using tools like lasers or plasma cutters.
- Bending: The process of deforming metal sheets into specific angles or curves.
- Welding: Joining two or more metal pieces together through heat or pressure.
- Assembly: The final stage where fabricated parts are put together to form complete structures.
Applications of Metal Fabrication in the Oil & Gas Industry
Metal fabrication serves various functions within the oil and gas industry. Below are some of the primary applications:
1. Drilling Equipment
Drilling operations are at the heart of oil extraction. Metal fabrication is used to produce:
- Drill Bits: Essential tools that penetrate rock formations. They must be durable to withstand high temperatures and pressures.
- Casing: Steel pipes that line the drilled hole to prevent collapse and protect groundwater.
- Wellheads: Equipment installed at the surface of an oil or gas well to control pressure and flow.
2. Pipelines
Pipelines are critical for transporting crude oil and natural gas from extraction sites to processing facilities. Key aspects include:
- High-Pressure Steel Pipes: Designed to handle extreme pressures and corrosive materials.
- Custom-Fabricated Fittings: Ensuring seamless connections between pipeline sections.
3. Storage Tanks
Storage tanks are necessary for holding crude oil and refined products before distribution. Fabrication involves:
- Large Capacity Tanks: Built to exacting safety standards to prevent leaks and ensure structural integrity.
- Pressure Vessels: Used for storing gases or liquids under pressure.
4. Offshore Platforms
Offshore drilling requires robust platforms that can withstand harsh marine environments. Fabrication includes:
- Structural Steel Frameworks: Providing stability against waves and winds.
- Living Quarters: Facilities for workers on offshore rigs, fabricated with safety in mind.
The Importance of Quality in Metal Fabrication
In the oil and gas industry, quality is paramount due to safety concerns and regulatory requirements. Poorly fabricated components can lead to catastrophic failures, resulting in environmental disasters or loss of life. Therefore, companies must adhere to stringent quality control measures throughout the fabrication process.
Quality Control Measures
- Material Testing: Ensuring metals meet required specifications for strength and corrosion resistance.
- Welding Inspections: Verifying weld integrity through non-destructive testing methods.
- Compliance with Standards: Adhering to international standards such as ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) and API (American Petroleum Institute).
Advancements in Metal Fabrication Technology
Recent technological advancements have transformed metal fabrication processes, enhancing efficiency and precision. Some notable innovations include:
1. Computer Numerical Control (CNC)
CNC technology automates machinery for cutting, bending, and welding metals with high precision. Benefits include:
- Increased Production Speed: Faster turnaround times for projects.
- Customization Capabilities: Ability to create complex designs tailored to specific needs.
2. Additive Manufacturing
Also known as 3D printing, this technology allows for rapid prototyping and production of intricate components that traditional methods may struggle with.
3. Robotics
The use of robotic systems in welding and assembly processes improves consistency while reducing human error.
Challenges Facing Metal Fabrication in Oil & Gas
Despite its importance, the metal fabrication sector faces several challenges:
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Global events can impact the availability of raw materials needed for fabrication.
- Skilled Labor Shortages: A lack of trained professionals can hinder production capabilities.
- Environmental Regulations: Increased scrutiny on environmental impacts requires companies to adopt sustainable practices.
Future Trends in Metal Fabrication for Oil & Gas
The future of metal fabrication in the oil and gas industry will likely see continued evolution driven by innovation:
1. Sustainability Practices
As environmental concerns grow, there will be a push towards sustainable materials and practices within metal fabrication processes.
2. Enhanced Automation
Further integration of automation technologies will streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve safety outcomes.
3. Digital Twin Technology
This involves creating virtual replicas of physical assets to optimize performance through real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance strategies.
Metal fabrication is an indispensable aspect of the oil and gas industry, underpinning every phase from exploration to transportation. As technology continues to advance, so too will the capabilities within this sector, ensuring that it meets both current demands and future challenges effectively. By focusing on quality, innovation, and sustainability, metal fabrication will remain a cornerstone of success in the ever-evolving landscape of oil and gas operations.
What are the latest advancements in metal fabrication technology for the oil and gas industry?
The oil and gas industry is undergoing significant transformations driven by advancements in metal fabrication technology.
These innovations enhance efficiency, safety, and sustainability, which are crucial in an industry that constantly faces challenges such as fluctuating oil prices, environmental regulations, and the need for rapid productionBelow we will explore the latest advancements in metal fabrication technology specifically tailored for the oil and gas sector.
Key Advancements in Metal Fabrication Technology
1. Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Systems
CNC technology has revolutionized metal fabrication by automating and controlling manufacturing processes with high precision. This advancement allows for:
- Increased Production Speed: CNC systems can operate continuously, significantly reducing lead times.
- Design Flexibility: They enable manufacturers to create complex designs that meet specific requirements without extensive retooling.
- Consistency and Quality: Automated processes minimize human error, ensuring that each component meets stringent industry standards.
2. Fiber Laser Cutting Technology
Fiber laser cutting has emerged as a preferred method due to its superior performance compared to traditional CO₂ lasers. Key benefits include:
- Higher Precision: Fiber lasers provide unmatched cutting accuracy, which is essential for producing components with tight tolerances required in oil and gas applications.
- Efficiency with Reflective Metals: Unlike traditional lasers, fiber lasers can cut reflective materials like aluminum and brass effectively.
- Reduced Waste: The precision of fiber lasers minimizes material waste during production, aligning with sustainability goals.
3. Robotic Welding Systems
The integration of robotics into welding processes is transforming metal fabrication. Advantages include:
- Consistency and Quality: Robotic systems deliver uniform welds with high repeatability, reducing the risk of defects.
- Speed: Robots can perform welding tasks faster than manual methods, increasing overall productivity.
- Safety Improvements: By taking over hazardous welding tasks, robots enhance workplace safety for human workers.
4. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
3D printing is becoming increasingly important in metal fabrication for the oil and gas industry. Its advantages are:
- Complex Geometries: 3D printing allows for the creation of intricate parts that would be difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods.
- Rapid Prototyping: It enables quick iterations on design concepts, significantly speeding up the development process.
- Material Efficiency: Additive manufacturing uses only the necessary amount of material, reducing waste and costs.
5. Smart Manufacturing and IoT Integration
The adoption of smart manufacturing practices is reshaping the metal fabrication landscape. Key features include:
- Real-Time Monitoring: IoT devices collect data from machinery to monitor performance and predict maintenance needs, reducing downtime.
- Data Analytics: Advanced analytics help optimize production processes by identifying inefficiencies and suggesting improvements.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms analyze operational data to forecast equipment failures before they occur, enhancing reliability.
Sustainability Initiatives in Metal Fabrication
With increasing pressure to reduce environmental impacts, the oil and gas industry is focusing on sustainable practices within metal fabrication:
1. Eco-Friendly Coating Solutions
Innovations in coating technologies are leading to environmentally friendly options such as low-VOC (volatile organic compounds) finishes and powder coatings that enhance durability while minimizing environmental impact.
2. Recycling and Waste Reduction
Metal fabricators are adopting practices that prioritize recycling scrap metal and utilizing energy-efficient equipment to reduce their carbon footprint. This shift not only meets regulatory requirements but also appeals to environmentally conscious clients.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite these advancements, the metal fabrication industry faces challenges such as rising raw material costs and a shortage of skilled labor. However, ongoing innovations provide pathways to overcome these obstacles:
- Investment in Training: Companies are increasingly investing in training programs to upskill workers in advanced technologies like CNC machining and robotics.
- Reshoring Manufacturing: The trend towards reshoring is gaining momentum as companies seek reliable domestic suppliers to mitigate supply chain disruptions experienced during global crises.
The latest advancements in metal fabrication technology are significantly enhancing the capabilities of the oil and gas industry. From CNC systems and fiber laser cutting to robotic welding and 3D printing, these innovations are driving efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
How is fiber laser technology changing the metal fabrication process in the oil and gas industry?
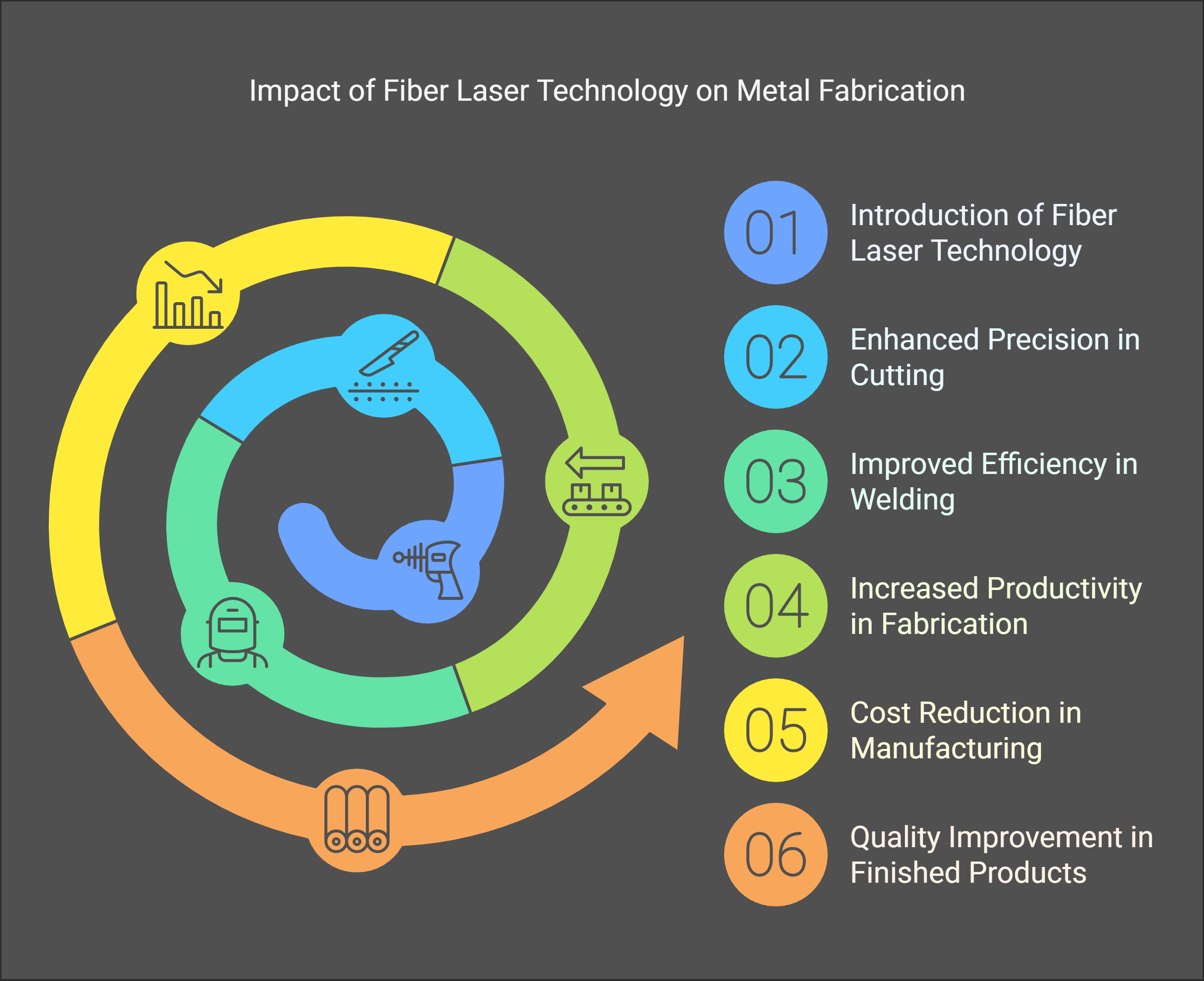
Fiber laser technology is revolutionizing metal fabrication processes across various industries, particularly in the oil and gas sector.
This advanced cutting method offers significant improvements in precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, making it an essential tool for manufacturers involved in this critical industry. Here’s a detailed look at how fiber laser technology is transforming metal fabrication in the oil and gas industry.
Key Features of Fiber Laser Technology
Fiber lasers utilize optical fibers doped with rare-earth elements to generate high-intensity laser beams. This technology presents several advantages over traditional laser systems, such as CO₂ lasers:
- Higher Efficiency: Fiber lasers convert a greater percentage of electrical energy into laser light, often exceeding 30% wall-plug efficiency, which translates to lower energy consumption and reduced operational costs.
- Minimal Maintenance: With fewer moving parts and a robust design, fiber lasers require less maintenance compared to traditional systems, leading to reduced downtime and lower operational costs.
- Superior Beam Quality: The focused laser beam allows for exceptional cutting precision and quality, producing clean edges with minimal heat-affected zones (HAZ). This feature is crucial in the oil and gas industry, where component integrity is vital.
Applications of Fiber Laser Technology in Oil and Gas
1. Precision Cutting of Components
Fiber lasers excel at cutting various metals used in the oil and gas industry, including stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium. Their ability to create intricate designs with tight tolerances is invaluable for:
- Pipelines: The construction of pipelines requires precision to prevent leaks and ensure safety. Fiber lasers can cut pipe sections accurately, ensuring that joints fit perfectly.
- Valves and Flanges: These components often have complex geometries that demand high precision. Fiber lasers can produce these parts with minimal waste and high accuracy.
2. Efficient Welding Processes
Welding is a critical operation in the oil and gas sector, particularly for large fuel pipes that require strong joints capable of withstanding high pressures. Fiber laser welding offers:
- Automated Solutions: The automation capabilities of fiber lasers streamline the welding process, allowing for consistent quality across multiple welds.
- Strong Welds: The high energy concentration of fiber lasers produces welds that are not only strong but also have a reduced risk of defects compared to traditional welding methods.
3. Laser Cleaning Applications
Oil and gas facilities are prone to contamination from dust, sludge, and rust. Fiber laser cleaning technology provides a non-abrasive method for maintaining equipment by effectively removing contaminants without damaging surfaces.
4. Permanent Marking Solutions
Fiber lasers are also used for marking components permanently. This is crucial for tracking parts throughout their lifecycle in complex systems like pipelines and machinery.
Advantages of Fiber Laser Technology
The adoption of fiber laser technology brings several benefits specifically tailored to the needs of the oil and gas industry:
- Increased Productivity: Fiber lasers can operate at speeds up to three times faster than traditional CO₂ lasers, significantly enhancing production rates while reducing lead times.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Although the initial investment may be higher, the long-term savings from lower energy consumption, reduced maintenance costs, and increased throughput make fiber lasers a financially sound choice.
- Versatility: Fiber lasers can cut through a wide range of materials effectively, allowing manufacturers to handle diverse projects without needing multiple machines.
Case Studies: Impact on Operations
Several companies in the oil and gas sector have reported significant improvements after integrating fiber laser technology into their fabrication processes:
- Pipeline Construction: A major pipeline manufacturer adopted fiber laser cutting for their operations, resulting in improved accuracy in component fabrication. This change led to a reduction in pipeline leaks during testing phases, enhancing overall safety.
- Maintenance Operations: An oil refinery implemented fiber laser cleaning technology to maintain equipment integrity. The results showed improved efficiency in operations due to reduced downtime for cleaning processes.
Future Trends in Fiber Laser Technology
As technology continues to advance, several trends are expected to shape the future of fiber laser applications in the oil and gas industry:
- Integration with AI: The incorporation of artificial intelligence into fiber laser systems will enable predictive maintenance capabilities and optimize cutting processes based on historical data.
- Sustainability Focus: With increasing environmental regulations, the oil and gas industry will likely continue moving towards more sustainable practices. Fiber lasers contribute positively by reducing waste and energy consumption during fabrication processes.
Fiber laser technology is fundamentally changing metal fabrication processes within the oil and gas industry by enhancing precision, efficiency, and sustainability.
As companies increasingly adopt this advanced technology, they can expect improved operational performance while meeting stringent safety standards. The ongoing evolution of fiber laser applications promises even greater advancements in manufacturing capabilities as the industry adapts to new challenges and opportunities.