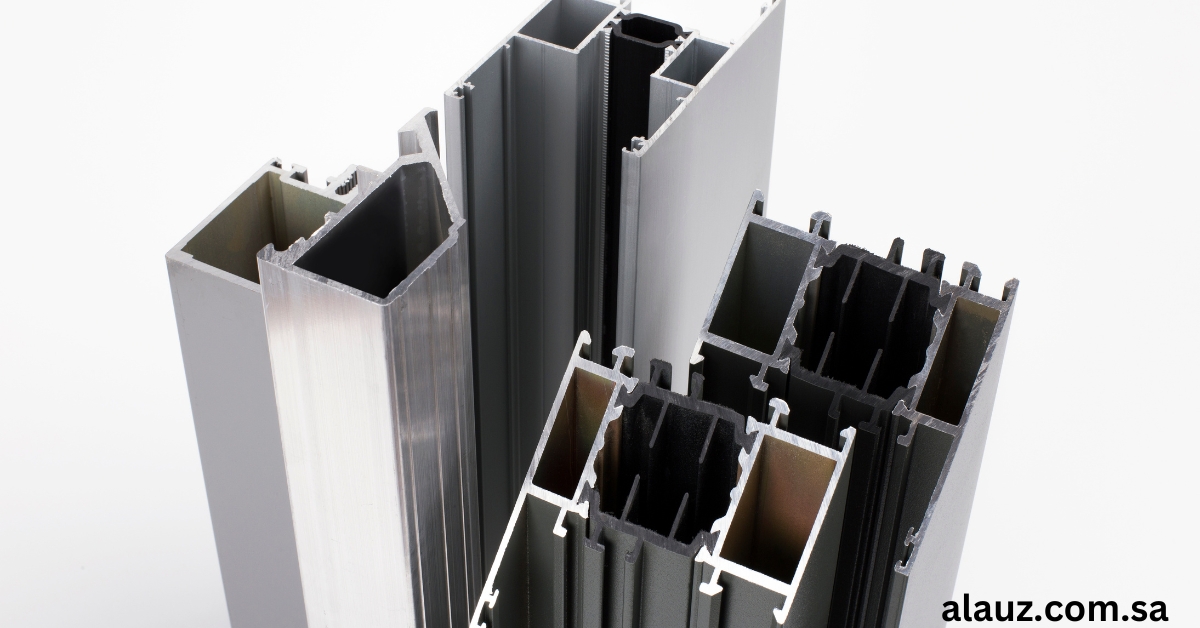
Metal fabrication is a crucial process in various industries, ranging from construction to aerospace. The choice of metal significantly affects the performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness of the final product.
In this blog article, we will explore the most common metals used in fabrication, their unique properties, and the benefits they offer.
Understanding Metal Fabrication
Metal fabrication involves the creation of metal structures by cutting, bending, and assembling processes. The choice of material is essential as it influences the strength, weight, corrosion resistance, and overall functionality of the fabricated item. Below are some of the most commonly used metals in fabrication.
Common Metals in Fabrication
Steel
Steel is an alloy primarily composed of iron and carbon. It is one of the most widely used metals in fabrication due to its remarkable strength and versatility.
Types of Steel
- Carbon Steel: Contains varying amounts of carbon, which affects its hardness and tensile strength. It’s known for its durability and is widely used in construction and manufacturing.
- Stainless Steel: This type includes chromium, which provides excellent corrosion resistance. It is commonly used in kitchen appliances, medical instruments, and construction materials due to its aesthetic appeal and durability.
| Type of Steel | Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Strong, durable | Construction, automotive parts |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion-resistant, aesthetic appeal | Kitchenware, medical instruments |
Aluminum
Aluminum is a lightweight metal known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio. It is highly malleable and resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for various applications.
Benefits of Aluminum
- Lightweight: Approximately one-third the weight of steel, making it suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical.
- Corrosion Resistance: Forms a protective oxide layer that prevents further oxidation.
- Recyclability: Can be recycled multiple times without losing quality.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight (1/3 that of steel) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent; forms protective oxide layer |
| Recyclability | 100% recyclable without quality loss |
Copper
Copper is known for its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity. It is ductile and malleable, making it easy to work with during fabrication.
Applications of Copper
- Electrical Wiring: Due to its high conductivity.
- Plumbing: Used in pipes and fittings due to its resistance to corrosion.
Brass
Brass is an alloy made primarily from copper and zinc. It offers good machinability and corrosion resistance.
Advantages of Brass
- Acoustic Properties: Ideal for musical instruments due to its sound quality.
- Malleability: Easy to form into various shapes.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Composition | Copper and Zinc |
| Machinability | Excellent; can be easily shaped |
| Acoustic Properties | Ideal for musical instruments |
Bronze
Bronze is another copper alloy that includes tin or other elements. It is known for its toughness and resistance to corrosion.
Benefits of Bronze
- Durability: More durable than pure copper.
- Corrosion Resistance: Performs well in marine environments.
Advantages of Using These Metals
Each metal used in fabrication offers distinct advantages that cater to specific needs:
1. Strength and Durability
Metals like steel provide exceptional structural integrity, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications such as construction and machinery.
2. Corrosion Resistance
Materials like stainless steel and aluminum resist rusting and degradation from environmental factors, extending their lifespan.
3. Malleability and Workability
Aluminum, brass, and bronze can be easily shaped into complex designs without compromising their structural integrity.
4. Lightweight Options
Aluminum’s low density makes it ideal for applications where weight reduction is essential, such as in the aerospace industry.
Selecting the right metal for fabrication depends on various factors including strength requirements, environmental conditions, cost considerations, and specific application needs. Understanding the properties and benefits of common metals like steel, aluminum, copper, brass, and bronze can help manufacturers make informed decisions that enhance product performance while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
What are the unique benefits of using copper in metal fabrication?
Copper is a versatile and widely used metal in various industries, particularly in metal fabrication. Its unique properties make it an ideal choice for numerous applications, ranging from electrical components to architectural features.
Below we will outlines the distinctive benefits of using copper in metal fabrication, highlighting its exceptional conductivity, antimicrobial properties, workability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal.
Exceptional Electrical and Thermal Conductivity
One of the most significant advantages of copper is its outstanding electrical and thermal conductivity.
- Electrical Conductivity: Copper is renowned for being one of the best conductors of electricity, second only to silver. This property makes it indispensable in electrical applications such as wiring, circuit boards, and connectors. Its ability to efficiently transfer electrical currents ensures minimal energy loss, making devices more efficient and eco-friendly.
- Thermal Conductivity: Copper also excels in thermal conductivity, which allows it to dissipate heat effectively. This characteristic is crucial in applications like heat exchangers and cooling systems, where efficient heat transfer is necessary to maintain optimal operating conditions.
Antimicrobial Properties
Copper possesses natural antimicrobial properties that inhibit the growth of bacteria and other pathogens. This feature is particularly beneficial in industries where hygiene is paramount:
- Healthcare Applications: Copper’s antimicrobial qualities make it an excellent choice for medical equipment, hospital surfaces, and touchpoints in healthcare settings. Using copper can help reduce the spread of infections by minimizing microbial contamination.
- Food Processing: In food processing environments, copper’s antimicrobial properties contribute to safer surfaces for food preparation and storage, enhancing overall hygiene standards.
Excellent Workability
Copper is highly malleable and ductile, which allows it to be easily shaped and formed into complex designs without cracking or breaking. This workability offers several advantages:
- Fabrication Processes: Copper can be easily processed through various methods such as rolling, stamping, extruding, and forging. Its ability to be shaped into intricate forms makes it suitable for a wide range of applications—from decorative elements to functional components.
- Versatile Applications: The malleability of copper enables its use in diverse products such as wires, pipes, roofing materials, and decorative fixtures. This versatility makes it a preferred material across multiple industries.
Corrosion Resistance
While copper can corrode under certain conditions, its overall corrosion resistance is superior compared to many other metals.
- Longevity: Copper’s resistance to corrosion allows it to withstand harsh environments without degrading quickly. This property is particularly advantageous for outdoor applications such as roofing and plumbing systems where exposure to moisture and air can lead to deterioration.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: The durability afforded by copper’s corrosion resistance translates into lower maintenance costs over time. Components made from copper require less frequent replacement compared to those made from less resistant materials.
Aesthetic Appeal
Copper’s distinctive reddish-brown color and ability to develop a patina over time add aesthetic value to any project.
- Architectural Features: In architecture, copper is often used for roofing, gutters, and decorative elements due to its visual appeal. The natural patina that forms on copper surfaces not only enhances its beauty but also provides additional protection against corrosion.
- Design Flexibility: The ability to manipulate copper into various shapes while maintaining its aesthetic qualities makes it a popular choice among designers and architects looking for both functionality and beauty in their projects.
Summary Table of Benefits
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Excellent conductor of electricity; minimal energy loss |
| Thermal Conductivity | Efficient heat transfer; ideal for cooling systems |
| Antimicrobial Properties | Reduces bacterial growth; enhances hygiene in medical and food applications |
| Workability | Highly malleable; easy to shape into complex designs |
| Corrosion Resistance | Durable; withstands harsh environments; lower maintenance costs |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Unique color; develops protective patina; visually appealing |
Copper’s unique combination of properties makes it an invaluable material in metal fabrication across various industries. Its exceptional electrical and thermal conductivity ensures efficient performance in electrical applications, while its antimicrobial properties enhance hygiene standards in healthcare and food processing settings. The metal’s excellent workability allows for versatile applications without compromising structural integrity.