Metal fabrication is an essential industry that involves shaping and assembling metal components for various applications, from construction to automotive manufacturing.
However, the nature of this work exposes fabricators to numerous hazards, including sharp tools, heavy machinery, and toxic substances. Ensuring workplace safety is paramount not only for compliance with regulations but also for the well-being of employees.
In this blog article, we will provide in-depth safety tips tailored specifically for metal fabricators, emphasizing best practices and expert advice.
Understanding the Risks in Metal Fabrication
Before delving into safety tips, it’s crucial to recognize the inherent risks associated with metal fabrication. These include:
- Sharp Tools and Equipment: The use of cutting tools can lead to severe lacerations or puncture wounds.
- Heavy Machinery: Operating machines like shears and presses can result in crush injuries if proper precautions are not taken.
- Toxic Fumes: Welding and cutting metals release harmful fumes that can affect respiratory health.
- Noise Exposure: Prolonged exposure to high noise levels can cause hearing loss.
Essential Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Wearing appropriate PPE is the first line of defense against workplace hazards. Key items include:
- Safety Goggles: Protect eyes from flying debris and harmful UV rays during welding.
- Cut-Resistant Gloves: Essential for preventing cuts when handling sharp materials.
- Steel-Toed Boots: Protect feet from heavy objects and provide slip resistance.
- Respirators or Dust Masks: Necessary when working in environments with airborne particles or fumes.
Best Practices for Tool Safety
Proper tool usage and maintenance are critical in preventing accidents. Here are some best practices:
- Regular Inspections: Before use, inspect tools for any signs of damage or wear. Malfunctioning tools should be repaired or replaced immediately.
- Correct Usage: Always use tools for their intended purpose. Improvising can lead to accidents.
- Training on Tool Operation: Ensure all employees are trained on the correct operation of tools and machinery.
Safe Material Handling Techniques
Improper handling of materials is a common cause of injuries in metal fabrication. To mitigate risks:
- Use Mechanical Aids: Employ forklifts, hoists, or dollies to lift heavy materials instead of relying solely on manual lifting.
- Team Lifting: For large or awkward items, always use team lifting techniques to distribute weight evenly.
- Clear Pathways: Keep walkways and work areas free of clutter to prevent trips and falls.
Ventilation and Air Quality Management
Maintaining good air quality is vital in a metal fabrication shop. Consider these strategies:
- Install Ventilation Systems: Use exhaust fans and fume extraction systems to reduce airborne contaminants.
- Regular Air Quality Monitoring: Implement routine checks to ensure that air quality meets safety standards.
Fire Safety Precautions
Given the use of welding equipment, fire safety should be a top priority:
- Keep Fire Extinguishers Accessible: Ensure that fire extinguishers are easily accessible and regularly inspected.
- Train Employees on Fire Safety Protocols: Conduct regular training sessions on fire prevention measures and emergency response procedures.
Noise Control Measures
To protect workers from hearing damage:
- Use Hearing Protection: Provide earplugs or earmuffs in high-noise areas.
- Implement Noise Barriers: Where possible, install sound barriers around noisy equipment.
Creating a Safety Culture
Fostering a culture of safety within the workplace encourages employees to prioritize safety practices:
- Regular Training Sessions: Conduct ongoing training on safety protocols, tool usage, and emergency procedures.
- Encourage Reporting of Hazards: Create an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting unsafe conditions without fear of reprisal.
Incident Reporting and Analysis
Establishing a system for reporting incidents helps identify trends and prevent future accidents:
- Document All Incidents: Maintain records of all accidents, near misses, and unsafe conditions.
- Conduct Root Cause Analysis: After an incident occurs, analyze the causes to implement corrective actions.
Compliance with Safety Regulations
Staying compliant with local regulations is essential for maintaining a safe workplace:
- Understand OSHA Standards: Familiarize yourself with Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations relevant to metal fabrication.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular safety audits to ensure compliance with safety standards and identify areas for improvement.
Emergency Preparedness
Being prepared for emergencies can save lives:
- First Aid Training: Ensure that employees are trained in first aid and CPR.
- Emergency Response Plans: Develop clear emergency response plans for various scenarios (fires, chemical spills, etc.) and conduct drills regularly.
Safety in metal fabrication is a multifaceted issue that requires ongoing attention and commitment from all levels of an organization.
By implementing these workplace safety tips—ranging from proper PPE usage to creating a robust safety culture—metal fabricators can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries. Prioritizing safety not only protects workers but also enhances productivity and morale within the workplace.
What are the most common injuries in metal fabrication and how can they be prevented?
Metal fabrication is a vital industry that involves various processes such as cutting, bending, and assembling metal components.
While essential for manufacturing, it also poses significant risks to workers. Understanding the most common injuries in metal fabrication and implementing effective prevention strategies is crucial for ensuring a safe work environment. Below is an overview of prevalent injuries in this field and how they can be mitigated.
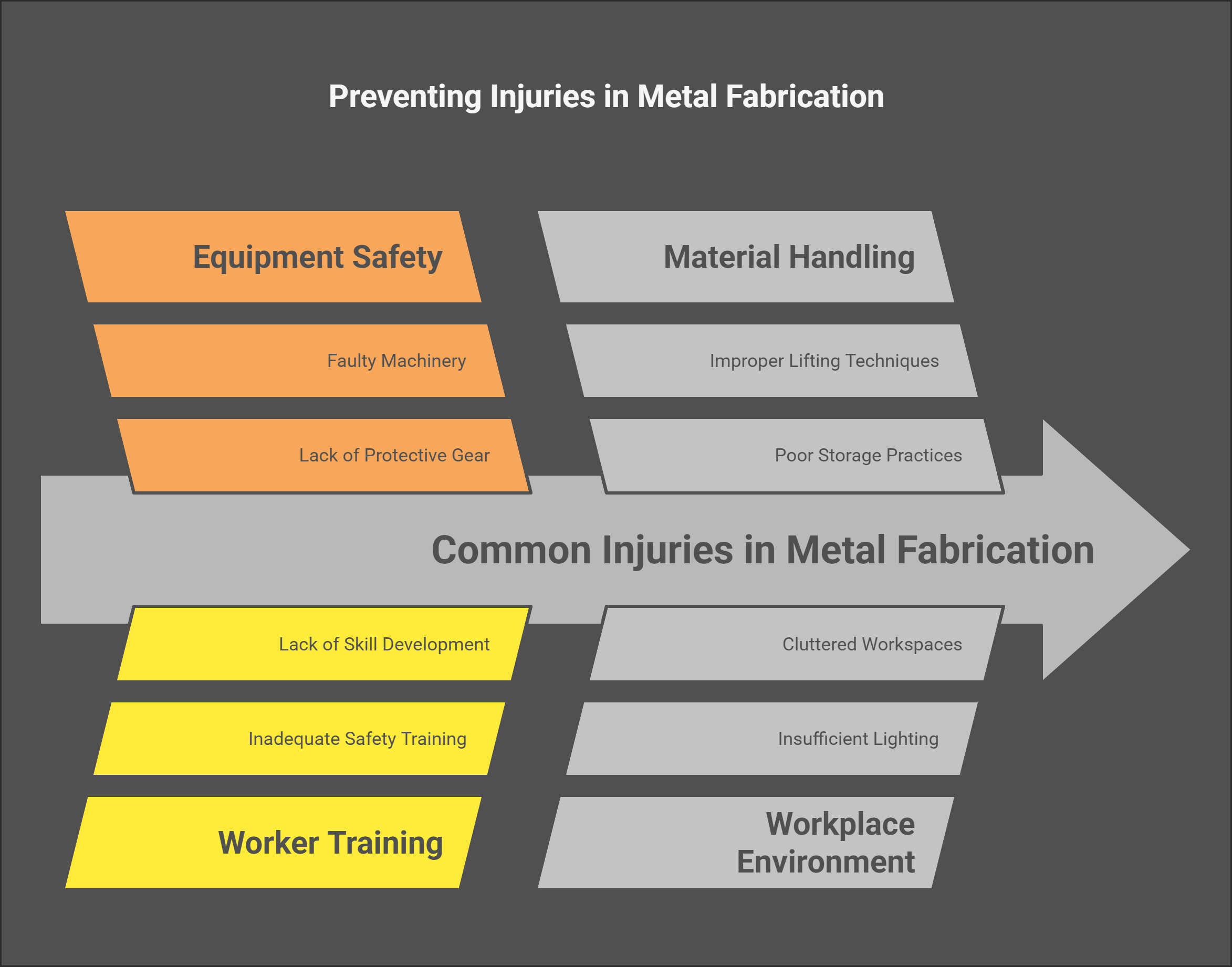
Common Injuries in Metal Fabrication
1. Musculoskeletal Injuries
Musculoskeletal injuries are among the most frequent in metal fabrication. These injuries often occur due to improper lifting techniques, repetitive motions, or awkward postures during tasks.
- Causes:
- Improper lifting of heavy materials.
- Repeated exposure to vibrations from tools.
- Prolonged awkward postures while working.
- Prevention:
- Proper Training: Educate workers on correct lifting techniques and the importance of posture.
- Mechanical Aids: Utilize forklifts, hoists, and trolleys to handle heavy materials, reducing the physical strain on workers.
- Ergonomic Workstations: Design workstations that promote good posture and reduce strain.
2. Cuts and Lacerations
Cuts and lacerations are common injuries resulting from sharp tools and materials used in metal fabrication.
- Causes:
- Handling sharp metal sheets or tools without proper protective gear.
- Poorly maintained or defective tools.
- Prevention:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Ensure all workers wear cut-resistant gloves and safety goggles to protect against sharp edges.
- Tool Maintenance: Regularly inspect tools for defects and replace them as necessary to prevent accidents.
3. Eye Injuries
Eye injuries can occur from flying debris, sparks during welding, or exposure to harmful chemicals.
- Causes:
- Lack of eye protection when operating machinery or performing welding tasks.
- Prevention:
- Safety Glasses/Goggles: Mandate the use of appropriate eye protection that meets safety standards.
- Training on Hazards: Provide training on the importance of wearing eye protection and recognizing potential hazards.
4. Hearing Loss
Prolonged exposure to high noise levels from machinery can lead to hearing loss over time.
- Causes:
- Operating loud machinery without adequate hearing protection.
- Prevention:
- Hearing Protection: Provide earplugs or earmuffs in areas where noise levels exceed safe thresholds.
- Noise Control Measures: Implement engineering controls such as sound barriers or soundproofing in high-noise areas.
5. Burns
Burns can result from hot surfaces, sparks, or molten metal during welding processes.
- Causes:
- Inadequate protective clothing or failure to follow safety protocols when handling hot materials.
- Prevention:
- Flame-Resistant Clothing: Require workers to wear flame-resistant gloves and aprons when welding or handling hot materials.
- Proper Training: Train employees on safe practices for handling hot materials and emergency response for burn incidents.
6. Respiratory Issues
Workers may be exposed to harmful fumes and dust generated during cutting, welding, or grinding processes.
- Causes:
- Inadequate ventilation leading to the accumulation of toxic fumes.
- Prevention:
- Ventilation Systems: Install effective ventilation systems to ensure proper airflow and reduce airborne contaminants.
- Respirators: Provide respirators equipped with appropriate filters for specific tasks involving hazardous materials.
Injuries in metal fabrication can have serious consequences for workers’ health and safety. By understanding the common types of injuries—such as musculoskeletal injuries, cuts, eye injuries, hearing loss, burns, and respiratory issues—employers can take proactive steps to mitigate these risks.
Implementing comprehensive training programs, enforcing the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), maintaining equipment properly, and fostering a culture of safety are essential strategies for preventing injuries in this demanding industry. Prioritizing safety not only protects employees but also enhances productivity and morale within the workplace.
What are the most effective safety measures to prevent musculoskeletal injuries in metal fabrication?
Musculoskeletal injuries (MSIs) are a significant concern in the metal fabrication industry, often resulting from the physical demands of the job.
These injuries can affect the back, neck, shoulders, and limbs, leading to discomfort, reduced productivity, and increased absenteeism.
To effectively prevent MSIs in metal fabrication, employers can implement a range of safety measures that focus on ergonomics, training, equipment use, and workplace organization.
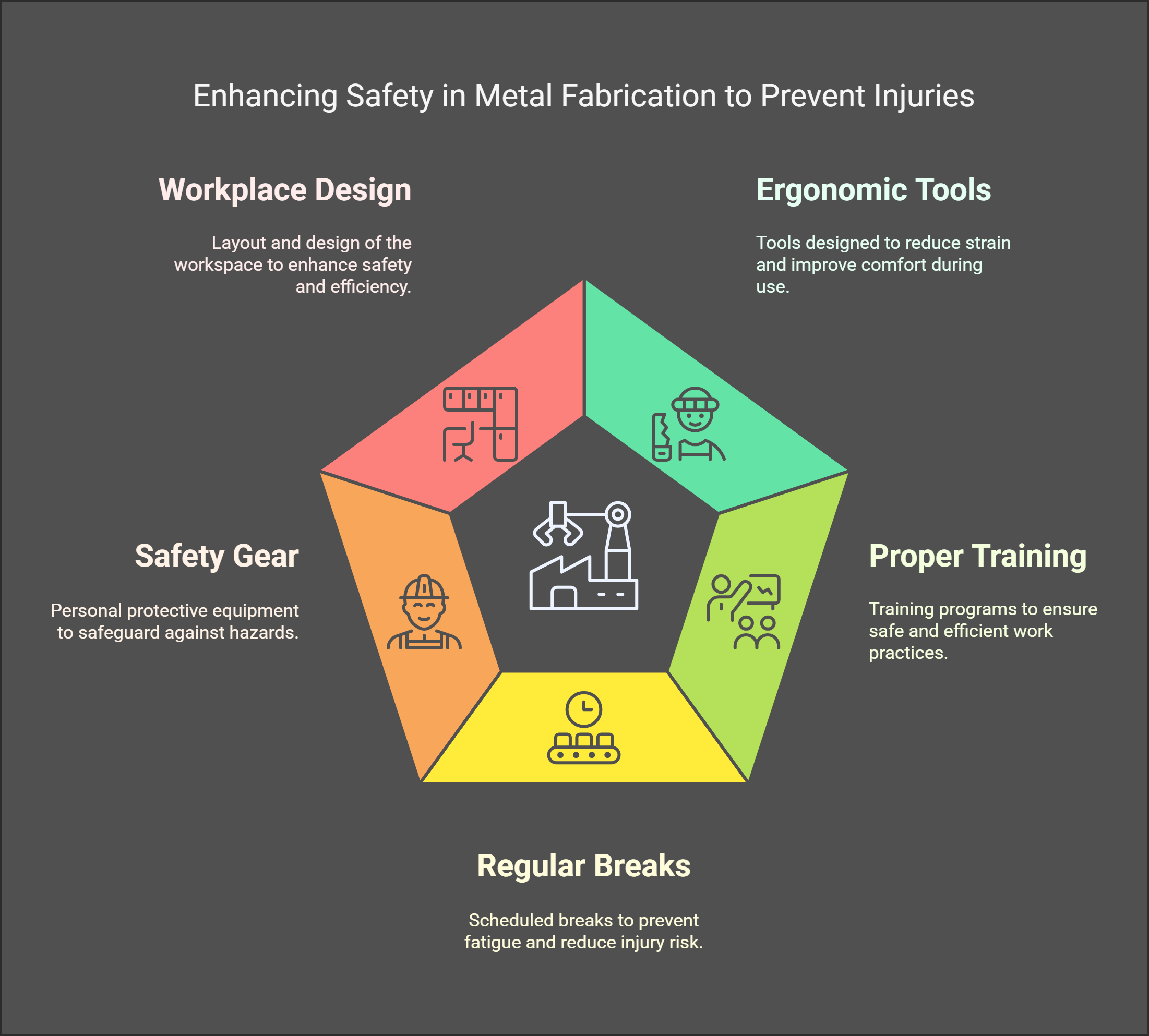
Effective Safety Measures to Prevent Musculoskeletal Injuries
1. Ergonomic Workstation Design
Creating ergonomic workstations is essential for reducing the risk of MSIs. This involves adjusting work areas to fit the physical needs of workers.
- Adjustable Workstations: Use height-adjustable tables and equipment to accommodate workers of different sizes and tasks. This helps minimize awkward postures during operations.
- Tool Placement: Position tools and materials within easy reach to avoid excessive stretching or bending. Tools should be organized to promote efficient workflow.
- Use of Ergonomic Tools: Invest in tools designed to reduce strain on hands and wrists. For example, tools with padded grips or those that require less force to operate can significantly decrease the risk of injuries.
2. Proper Training on Manual Handling Techniques
Training workers on safe lifting and handling techniques is crucial for preventing MSIs.
- Safe Lifting Practices: Teach employees to lift with their legs rather than their backs, keeping loads close to their bodies and avoiding twisting motions while lifting.
- Use of Mechanical Aids: Encourage the use of forklifts, hoists, and trolleys for transporting heavy materials instead of manual lifting whenever possible.
- Regular Refresher Courses: Conduct periodic training sessions to reinforce safe handling techniques and remind employees about the importance of ergonomics in their daily tasks.
3. Implementation of Scheduled Breaks
Fatigue can exacerbate the risk of MSIs. Regular breaks help reduce physical strain on workers.
- Scheduled Rest Periods: Implement mandatory breaks during shifts to allow workers to rest and recover from repetitive tasks or prolonged standing.
- Task Rotation: Encourage job rotation among employees to minimize repetitive strain on specific muscle groups and joints.
4. Regular Risk Assessments
Conducting regular assessments helps identify potential risks associated with specific tasks or work environments.
- Job Hazard Analysis: Evaluate each job role to identify movements or positions that pose an increased risk for MSIs. This includes analyzing lifting tasks, repetitive motions, and awkward postures.
- Adjustments Based on Findings: Use the information gathered from risk assessments to make necessary adjustments in workflows, equipment usage, or workstation design.
5. Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
While PPE is often associated with preventing cuts or burns, it can also play a role in reducing musculoskeletal injuries.
- Supportive Gear: Provide back supports or knee pads for tasks that involve heavy lifting or prolonged kneeling. This equipment can help alleviate stress on vulnerable areas.
- Proper Footwear: Ensure that employees wear appropriate footwear that provides support and cushioning for standing tasks.
6. Maintenance of Equipment
Well-maintained equipment reduces the likelihood of accidents that could lead to MSIs.
- Regular Inspections: Schedule routine maintenance checks for all machinery and tools to ensure they are functioning correctly and safely.
- Ergonomic Tools: Invest in ergonomic machinery that minimizes physical strain during operations. For instance, machines with adjustable heights can reduce bending or reaching.
7. Encouraging a Safety Culture
Fostering a culture of safety within the workplace encourages employees to prioritize their well-being.
- Open Communication: Encourage workers to report unsafe conditions or practices without fear of repercussions. This helps identify potential hazards early on.
- Recognition Programs: Implement programs that recognize safe practices among employees, promoting a culture where safety is valued and prioritized.
Preventing musculoskeletal injuries in metal fabrication requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses ergonomic design, proper training, scheduled breaks, regular assessments, effective use of PPE, maintenance of equipment, and fostering a safety culture.
By implementing these measures, employers can significantly reduce the risk of MSIs while enhancing overall worker health and productivity in the metal fabrication industry. Prioritizing employee well-being not only leads to a safer workplace but also contributes positively to operational efficiency and morale.